Stem Cell Types and Stem Cell Therapy
What is Stem Cell?
There are hundreds of different types of cells in our bodies that are important for our health. These cells are responsible for maintaining daily functions of our body, beating of our heart, functioning of our brain, cleansing of blood by our kidneys, regeneration of our skin, etc.
The unique task of stem cells is to produce all these different types of cells. They supply our new cells, producing them from themselves by dividing or from other types of cells. For example, stem cells in the skin can make more skin stem cells or differentiate into other skin cells that have a unique function, such as making melanin pigment.
The Importance of Stem Cells for Our Health
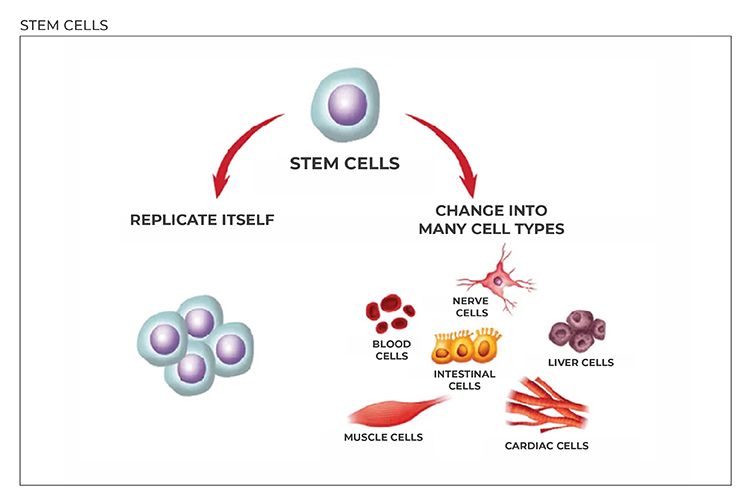
There are many different cells in our organs. If any cells in tissues or organs are damaged, stem cells turn into those cells and treat organs and tissues. They are responsible for regenerating damaged tissues and routinely replenishing other dying cells. They provide healing or regeneration in the region to where they head. Having unlimited ability to divide, stem cells are permanent protectors of our body.
Types of stem cell
Each type of cell has a structure and size compatible with its function. Cells with similar functionality form tissues and tissues form organs.
Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are cells in the embryo consisting of only 50 to 150 cells, which has only been fertilized a few days ago and has just begun to develop. These cells can differentiate into more than two hundred types of cells in our body.
Embryonic stem cells can reconstitute or clone a human being. Therefore, studies on embryonic stem cells are restricted for ethical reasons in all countries worldwide.
Importance of Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are a type of stem cell that is highly emphasized in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine because of its ability to transform into all kinds of cells and tissues found in living organisms and to divide unlimitedly.
Fetal Stem Cells
They are a type of stem cells usually isolated from an 8-12 week old fetus. They cannot rebuild a body, but they have the capacity to transform into almost all cells. They can be transferred to another person and used for therapeutic purposes worldwide. However, even though there is no concrete evidence, it is suspected that if they are replicated before they are delivered to another body, they carry the risk of causing tumor in the body to which they are transferred so scientists continue to do research studies related to such cells.
Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells are undifferentiated cells found among other cells in tissues and organs. They have the ability to self-renew and transform into the cells of the tissue or organ from which they originate.
Mesenchymal (Stromal) Stem Cells
Mesenchymal stem cells isolated from an adult have the ability to transform into, according to current knowledge, about 100 different cells, including bone, cartilage, muscle, nerve, liver, pancreas cells. Not only do they repair the damage in their own tissue but they also pass to another damaged tissue and repair it. They originate from connective tissue so they can contribute to the development and function of related tissue cells.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSC)
Other non-stem cells can be reprogrammed into stem cells. Stem cells obtained in this way are called induced (stimulated) stem cells. It is not ethically controversial as embryos are not used to generate them.
With the spread of induced pluripotent human stem cells, embryonic stem cells have been accepted as the gold standard rather than a research tool. This is due to the fact that therapies conducted using embryonic cells can now be performed using IPSC.
What is Stem Cell Therapy?
The basis of stem cell therapy is based on the principle of utilizing stem cells to regenerate tissues or organs by replenishing damaged or dying cells in the individual. It is a treatment method conducted for the purposes of remedying damage caused by various diseases on organs, preventing premature aging, etc.
How is stem cell therapy conducted?
It has now been discovered that stem cells and tissues isolated from our bodies can be replicated in the laboratory. Thus, stem cells can be used in aesthetic and rejuvenation applications as well as in the treatment of many diseases.
Which type of cell can be used in the disease treatment, the protocol of use and the success rate are completely person-specific.
Replication of stem cells and tissues in the laboratory requires a high level of technology, infrastructure, experience and is costly. For this reason, stem cell production suitable for clinical use is carried out in a limited number of centers worldwide. This procedure should be performed in accordance with GMP "Good Manufacturing Practices" system, which is a recognized system to ensure quality standards worldwide.
How are stem cells collected?
Apart from their isolation from the fetus and umbilical cord, when they'll be collected from a person's own body, the method of collection varies according to the region and the treatment in which stem cells will be used.
They can be obtained by surgically removing a small piece of tissue, removing a small amount of fat from the abdomen by liposuction, surgically removing bone marrow from hip bone and collecting blood from the vein.
How is stem cell transfer performed?
Although this procedure varies according to the type of treatment to be applied, stem cells can be directly introduced into the blood circulation system by intravenous method or directly injected into the damaged tissue or organ which needs to be treated and rejuvenated.
Which diseases can be cured with stem cells?
Since the natural task of stem cells is to replenish dying or damaged cells, scientists have considered applying stem cell therapy for various medical conditions. The basic idea is to make a patient healthy again by transferring stem cells or differentiated cells derived from stem cells to the patient and utilizing natural rejuvenating and regenerating properties of stem cells.
Some of the current promising research areas of stem cell therapy are listed below:
- Autism
- Oligospermia
- Infertility
- Impotence
- Cirrhosis
- MS (Multiple Sclerosis)
- Lupus Erythematosus
- Alzheimer
- Parkinson's
- Cerebral Palsy
- Facial Stem Cell Treatment
- ALS
- Rejuvenation with Stem Cells
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Heart Diseases
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Dementia
- Autoimmune Diseases
- LYME
- Orthopedic diseases
- Cerebral Ataxia
- Tooth and gum diseases
Related Content
Medical Aesthetics
With the non-surgical aesthetic applications, also known as medical aesthetics, it is possible to achieve the beauty you desire in minutes.
Read MoreFat Injection With Stem Cells
Nowadays, thanks to the developing technology, the excess fat removed from your body is enriched with your stem cells which have been isolated from that fat and injected to[...]
Read MoreStem Cell In Gingival Recession
Gingival recession is a common problem that can be observed at any age. Most people may not initially notice that there is withdrawal of the gums, because gum withdrawal[...]
Read More