Stem Cell In Gingival Recession
Gum recession is a common problem that can be observed at any age. Most people may not initially notice that they have gum recession because gum recession progresses slowly.

Gum recession may arise for a number of reasons. If the reason for weak gums is not prevented and if weak gums are not treated, they may cause severer problems over time. The tooth may begin to move away from the gum, which leads to "cavities" around the tooth where plaques may accumulate. If left untreated, these cavities deepen and the tooth may begin to move.
With stem cell treatment, your fibroblast cells, which form the basis of gums, are replicated in the laboratory and injected back, thus they replace the missing cells and ensure regeneration and repair of the gum.
What is gum?
Gums, in other words gingiva, are attached to the jaw bone. It's a tissue that surrounds each tooth like a collar around its neck region and below the visible part. It protects tooth foundations and rich in blood vessels.
What is gum recession?
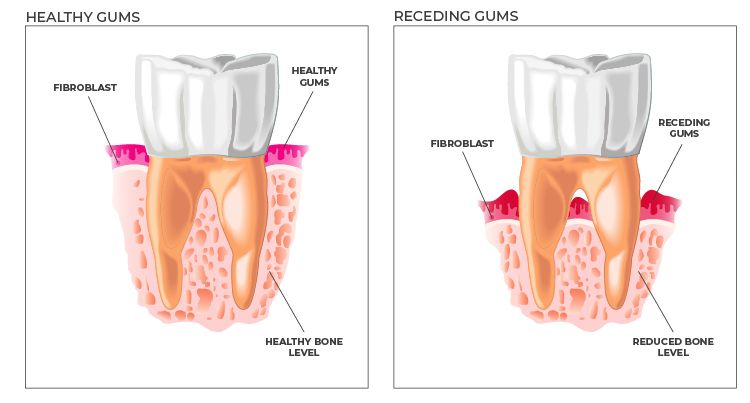
It's retraction of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth. As a result of this retraction, cavities or pockets form between the tooth and gumline. Disease-causing bacteria easily settle in these cavities.
If left untreated, gum recession may seriously damage bone structures and tissues supporting the teeth, which results in tooth loss.
What are the symptoms of gum recession?
- The first sign is mostly tooth sensitivity.
- Healthy gums are pinkish in color, while weak gums are red or swollen.
- They may bleed while you're eating hard food or for no reason.
- It may sometimes be a tooth that looks longer than normal.
- You may feel a notch on the tooth at the point where it's combined with the gum (gum line).
- Weak gums may also retract from your teeth and reveal the underlying root.
- In advanced cases, loose teeth may occur.
Why do gums recede?
Gum recession may occur at any age for a number of reasons, which primarily include the following:
Periodontal diseases:
The main cause of gum recession is infectious gum diseases that destroy bones and tissues.
Genetic factors:
Some people have inherited susceptibility, causing them to be more susceptible to gum diseases.
Incorrect and overzealous brushing: Incorrect or overzealous brushing may lead to abrasion of tooth enamel protecting the teeth and gum recession.
Poor dental care:
Reasons such as poor tooth brushing, not using antibacterial mouthwash and dental floss may cause plaque that will accumulate between teeth into gum stones, called tartar. These hard tartars that adhere to your teeth and gums can cause gum recession.
Hormonal changes:
Fluctuations in hormone levels pave the way for the gums to be more sensitive and thus gum recession.
Using tobacco products:
All tobacco users are at risk of having sticky plaques on their teeth that are difficult to remove. Tobacco use is a strong cause for tooth extraction as it also affects vascular health in the gums.
Teeth grinding and jaw clenching:
Sometimes, even without realizing it, grinding your teeth or clenching your jaw can apply too much force to your teeth, causing the gums to recede.
Misaligned teeth:
If the teeth are not properly aligned, too much pressure may be exerted on the teeth, gums, and bone, resulting in receding gums over time.
Lip or tongue piercing:
A piece of jewelry worn in these areas may come in contact with the gums and cause abrasion and irritation of the tissue.
How is gum recession treated?
If you suspect that your gums are weak or recede, the first thing to do is to consult a qualified dentist, as s/he can determine the cause and recommend the most appropriate treatment.
Scaling and plaque removal: Plaque and tartar below the gumline and on the root surface are removed by thorough cleaning by a dentist. The exposed root area is smoothed to make it difficult for the bacteria to adhere. Your dentist may also recommend antibiotics in order to get rid of the remaining harmful bacteria.
Gum surgery:
If a patient's condition is so severe that it causes excessive bone loss and very deep pockets, gum surgery may be necessary to repair the damage caused by gum recession.
Stem cell therapy:
It is a safe and easy method for the treatment of gum recession. Fibroblast cells, which are reproduced from a piece taken from your own gums, are replicated in special laboratories and injected back to your gums to regenerate and treat your gums. It can be applied alone or in combination with other treatments depending on your condition.
What are at risk of gum recession?
- Gum recession can be observed at any age, however, aging is considered as an important factor. Approximately 88% of people over the age of 65 years have gum recession in at least one tooth.
- People who use tobacco and tobacco products are also at a high risk of gum recession.
- The risk increases if the patient has a family history of gum recession. Because heredity is an important element in gum recession.
- Diabetes is a disease that increases the risk of gum recession.
What type of surgery is used to treat gum recession?
The methods of gum recession surgery your dentist will choose according to your individual needs are:
Open flap operation:
By folding back the affected gum tissue, harmful bacteria are removed from the pockets. The gum tissue is fixed firmly in place on the root of the tooth and the gaps formed are reduced.
Guided tissue regeneration: If there is damage due to gum recession, the method of recreating the lost bone and tissue can be utilized. After the gingival tissue is folded back and bacteria are removed, a regenerative material is applied to the area. Finally, the gum tissue is fixed to the tooth or root of the tooth again.
Soft tissue graft:
One of the methods used in the treatment is connective tissue graft. In this procedure, tissue is removed from the upper palate or another region and sutured to the gingival tissue surrounding the exposed root.
How to prevent gum recession?
- Perform full and regular dental care. Brush your teeth and floss every day.
- Brush your teeth correctly with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- If you smoke or use a tobacco product, quit it without delay.
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet.
- Keep track of changes in your mouth and do not neglect them.
- Visit your dentist at least once a year or as often as recommended.
Gum Treatment with Stem Cell
Stem cell therapy in gum recession is an application to replace your fibroblast cells, whose main task is to make your gum healthy and strong, which is diminished due to illness, over time or due to other factors.
Fibroblast cells are obtained from your own gums, replicated in special laboratories and injected back to you without adding any foreign substances, and they provide a natural treatment for your gums and have no side effects.
What are Stem Cells?
The task of stem cells, which are the basic cells that make up the tissues and organs in our body, is to provide regeneration and repair in a damaged tissue or organ by transforming into the respective cell of that tissue or organ.
They have the ability to divide indefinitely. They provide healing and regeneration in the region where they head to or where they are directed to without causing genetic errors.
Inside the gums, there are fibroblast cells specific to your gums. These cells help to keep the gums strong and healthy.
From where stem cells are removed in gum treatment?
Your fibroblast cells specific to your gum are obtained from a small piece of tissue that will be taken from your own gums for growth in special laboratories.
How is stem cell application carried out in gum?
The dentist removes a 3-4 mm tissue from gum and sends it to a special stem cell laboratory approved by the Ministry of Health. Under laboratory conditions, fibroblast cells that make up the gum are grown for 45 days.
Your cells generated are injected back into your gums every 30 days. The cells continue to multiply there and begin to repair your gums. This could completely prevent, abate or slow down your recession.
How long does it take?
In the first stage, the removal of tissue to be sent for stem cell generation takes a maximum of 15 minutes. It takes 30-45 days for the cells to grow in the stem cell laboratory approved by Ministry of Health. Therefore, the first application is performed 30-45 days after the removal of tissue, and the other 2 applications are about 1 month apart. Each application session takes about 1 hour.
Recovery after the application
Immediately after application, the process of proliferation and activation of the cells in the gum begins. However, the self-repair process of the gum takes place slowly so the maximum recovery effect is achieved 8-12 months later.
Does it have any side effects or does it cause any harm?
Since your own cells taken from your body are given back without any additives in the treatment, it has no risks such as incompatibility or allergic reaction. It has no side effects and does not cause any harm. It’s a safe and easy application.
Who can have this procedure?
Anyone who has no other health condition can have stem cell therapy for gum recession.
Related Content
Medical Aesthetics
With the non-surgical aesthetic applications, also known as medical aesthetics, it is possible to achieve the beauty you desire in minutes.
Read MoreFat Injection With Stem Cells
Nowadays, thanks to the developing technology, the excess fat removed from your body is enriched with your stem cells which have been isolated from that fat and injected to[...]
Read MoreStem Cell and Therapy
The main cells that make up the tissues and organs in our bodies are called stem cells. The role of stem cells, which are present in various forms in one organ, is to treat a[...][...]
Read More





